Reductions in births to teens and preterm birth rates are two
recent public health successes in the United States (1,2). From 2007 to 2014,
the birth rate for females aged 15–19 years declined 42%, from 41.5 to 24.2 per
1,000 females. The preterm birth rate decreased 8.4%, from 10.41% to 9.54% of
live births (1). Rates of preterm births vary by maternal age, being higher
among the youngest and oldest mothers. It is unknown how changes in the
maternal age distribution in the United States have affected preterm birth
rates. CDC used birth data to assess the relative contributions of changes in
the maternal age distribution and in age-specific preterm birth rates to the
overall decrease in preterm birth rates. The preterm birth rate declined in all
age groups. The effects of age distribution changes on the preterm birth rate
decrease were different in younger and older mothers. The decrease in the
proportion of births to mothers aged ≤19 and 20−24 years and reductions in
age-specific preterm rates in all age groups contributed to the overall decline
in the preterm birth rate. The increase in births to mothers aged ≥30 years had
no effect on the overall preterm birth rate decrease. The decline in preterm
births from 2007 to 2014 is related, in part, to teen pregnancy prevention and
the changing maternal age distribution. Effective public health strategies for
further reducing preterm birth rates need to be tailored to different age
groups.
National
Vital Statistics System data for all live births to U.S. residents in 2007 and
2014 were analyzed for the effects of maternal age on the decline in preterm
birth rates. The analysis was limited to births with gestational age ≥20 weeks,
as determined by the obstetric estimate. The year 2007 was the first year the
obstetric estimate was available nationally (1,3). The year 2014
was the most recent year with final birth data available at the time of
analysis. Preterm birth rates were defined as <37 completed weeks of
gestation and expressed as a percentage of live births. Maternal age was
categorized as ≤19, 20−24, 25−29, 30−34, and ≥35 years. Using rate
decomposition methods, the change in preterm birth rates from 2007 to 2014 was
divided into two components: 1) changes in the maternal age distribution, and
2) changes in the age-specific preterm birth rates (4). The two
components were calculated relative to each other; one was held constant (by
using the average value for the 2 years) as the observed variation in the other
component was assessed. The sum of the two components across the age groups
equaled the total preterm birth rate difference (4).
From
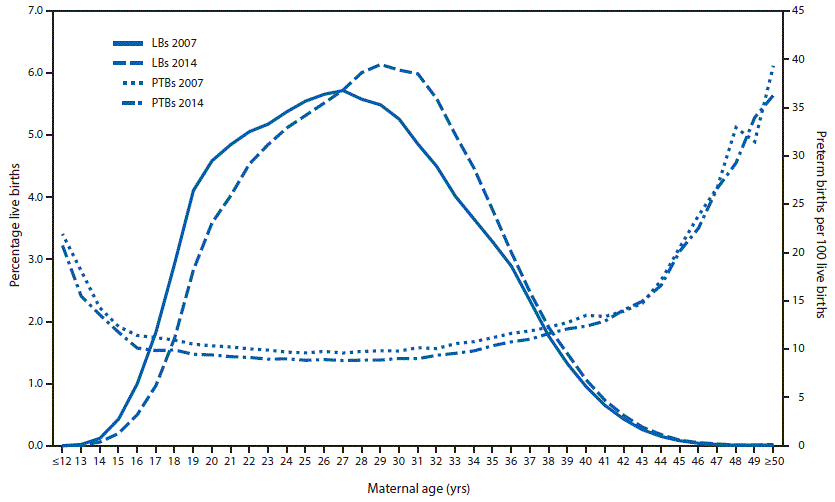
2007 to 2014, maternal age increased from a mean of 27.4 years to 28.3 years (Figure).
A decrease in the percentage of births to mothers aged ≤24 years was observed,
which included a 39.5% decrease in births to teens and an increase in births to
women aged ≥25 years (Table).
From
2007 to 2014, the preterm birth rate decreased from 10.41% to 9.54%, an
absolute rate difference of -0.87% (Table). A U-shaped relationship between maternal
age and preterm birth was present in both years with the lowest preterm birth
rate occurring among women aged 25−29 years (Table) (Figure). The decrease in
preterm birth rates from 2007 to 2014 was observed for mothers at all ages
<42 years. The absolute rate difference was highest among teens and lowest
among women aged ≥35 years (Table).
The
decomposition analysis partitioned the overall observed rate difference of
-0.87% into two parts, age distribution and age-specific rate components
(Table). The change in age distribution contributed to the preterm birth rate
decrease (as indicated by the negative values) only among mothers aged ≤24
years. In contrast, the age distribution component for mothers aged ≥25 years,
and especially for mothers aged ≥30 years, offset this decline. When the age
distribution components were summed across the age groups, a negligible effect
(0.01) was observed on the overall change in preterm birth rates. The change in
age-specific preterm birth rates contributed to the decline in preterm birth
rate across all age groups.
Examining
the total effect of both components on the preterm birth rate decline by age
group, the largest total effects were observed among mothers aged ≤19 and
mothers aged 20−24 years (Table). In these two groups, the change in age
distribution had a larger effect than the change in the age-specific preterm
birth rate. For mothers aged 25−29 years, the total effect also contributed to
the overall preterm birth rate decline because the age-specific rate component
was greater than the age distribution component. For mothers aged ≥30 years,
the total effect of both components did not contribute to the overall preterm
birth rate decrease; the rate increases from the age distribution components
were greater than the rate decreases from the age-specific rate components.
These
analyses included all births; however, sensitivity analyses restricting to
singleton births produced similar results. The overall absolute rate difference
for singletons during this period was -0.85%, compared with the -0.87% for all
births.
Discussion
The
overall decline in the preterm birth rate from 2007 to 2014 was related to
declines in age-specific preterm birth rates and a decrease in prevalence of
births to teens and women aged 20−24 years. The contribution from mothers aged
≥24 years to the age-distribution component was offset by an increased
prevalence of births to older mothers who have high rates of preterm birth.
Thus, the total age distribution component masked divergent influences of
younger and older mothers on the overall preterm birth rate decline. Because of
this, the influence of younger mothers on the overall preterm birth rate decline
is more appropriately indicated by examining the age-specific total effects in
the decomposition analysis. Considering relative effects of both age
distribution and age-specific preterm birth rate components, only mothers aged
≤29 years contributed to the overall rate decline, with the largest
contributions from teens and women aged 20−24 years.
Other
studies have documented increased preterm birth rates among teen and older
mothers compared with mothers in their mid-twenties to early thirties. Although
teen and older mothers might share some common preterm birth risk factors, such
as low socioeconomic status, extremes of body mass index, and smoking,
physiologic immaturity is a risk factor for teen mothers and the prevalence of
preexisting chronic disease is greater among older mothers. This heterogeneity
of risk for preterm births according to maternal age and the variation in
changes in age-specific preterm birth rates, combined with the changes in
maternal age distribution over time, suggest the need for varying preterm birth
prevention strategies across the reproductive life span.
The
findings in this report are subject to at least one limitation: the
relationship of preterm birth with maternal age is associative, not causal. The
analysis did not assess the impact of other pregnancy outcomes, such as
elective termination or fetal death, or of potential confounders, such as
maternal race/ethnicity, obstetric history, smoking, socioeconomic status, body
mass index, chronic or pregnancy-related conditions, prenatal care, and
delivery method. The effects on preterm birth rates of maternal
17-hydroxyprogesterone use, a preterm birth prevention strategy that increased
during this period , were not examined and the effects of maternal age on
spontaneous, medically indicated, early, or late preterm births were not
assessed.
The
overall decline in the preterm birth rate from 2007 to 2014 is related in part
to the changing maternal age distribution associated with the success of teen
pregnancy prevention and declines in unintended pregnancy. Teen pregnancy
prevention is one of CDC’s Winnable Battles . Although teen pregnancy
prevention and family planning have many positive health and societal effects,
the results of this analysis suggest these programs might also have direct
effects on reducing preterm birth rates. Based on recent data, 75% of
pregnancies to teens aged 15−19 years and 59% of pregnancies to women aged
20−24 years are unintended . The need for prevention of first and repeat teen
pregnancies continues. Prevention of unintended pregnancy and encouragement of
optimal birth spacing is one part of a five-part strategy for preterm birth
prevention. Other strategies include improved access to preconception care,
preterm birth risk identification and treatment, reduction of elective delivery
before 39 weeks gestation, and single embryo transfer in assisted reproductive
technology. These strategies need to be implemented throughout the reproductive
life span to reduce preterm births for all maternal ages.
FIGURE. Percentages of live births (LBs) and preterm births
(PTBs), by maternal age —United States, 2007 and 2014










![Ross & Wilson Anatomy and Physiology in Health and Illness by [Waugh, Anne, Grant, Allison]](https://images-eu.ssl-images-amazon.com/images/I/51-i7orjMpL.jpg)